Are Flocked Swabs Safe? Difference with Cotton Swabs
5982The flocked swab tip is generally made of polyester (polyester), polyamide (nylon), and other chemical synthetic fibers from the flocking process.
View detailsSearch the whole station Pandemic Supply
Flocked swabs are widely used for specimen collection due to their efficiency in collecting and releasing biological samples. Here’s a detailed look at their advantages, applications, and the procedure for using them:
Advantages of Flocked Swabs
Improved Sample Collection: The flocked fibers increase the surface area for sample collection, ensuring more cells or microorganisms are collected.
Efficient Release: The perpendicular fibers facilitate the complete release of the collected specimen into the transport medium.
Comfort: The soft, brush-like tip is more comfortable for patients compared to traditional fiber swabs.
Versatility: Suitable for various types of samples and tests, including PCR, antigen testing, and cultures.
Common Applications
Respiratory Sample Collection
Nasopharyngeal and oropharyngeal swabs for detecting respiratory viruses like COVID-19, influenza, and RSV.
Microbiological Testing
Wound, skin, and surface sampling for bacterial and fungal cultures.
DNA/RNA Collection
Buccal swabs for genetic testing, forensic analysis, and research.
Cell Collection
Collecting cells for cytological studies or other cellular analyses.
Procedure for Using Flocked Swabs
Preparation
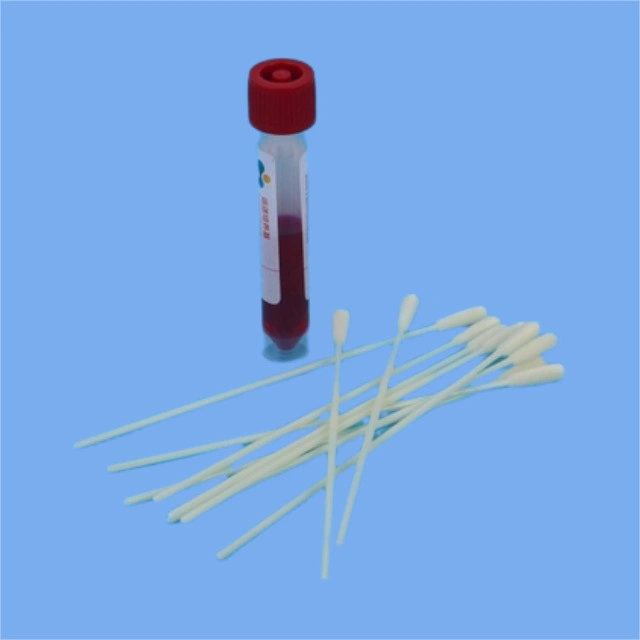
Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including gloves and a mask.
Ensure the swab and transport medium are sterile and within their expiration date.
Label the transport tube or collection container with the patient’s information.
Sample Collection
Nasopharyngeal Swab:
Tilt the patient’s head back slightly.
Insert the swab gently into one nostril, parallel to the palate, until resistance is met at the nasopharynx.
Rotate the swab several times to collect the specimen.
Oropharyngeal Swab:
Open the patient’s mouth and use a tongue depressor if necessary.
Swab the posterior pharynx and tonsillar areas, avoiding the tongue and teeth.
Buccal Swab:
Rub the swab against the inner cheek wall, rotating it to collect cells.
Transfer to Transport Medium
Place the swab into the transport medium or sterile container.
Break the swab shaft at the designated break point if necessary and securely close the container.
Transport and Storage
Place the collected sample in a biohazard bag or transport container.
Transport the sample to the laboratory as per guidelines, typically maintaining it at refrigerated temperatures (2-8°C).
Storage and Handling
Store unused swabs in their original, unopened packaging at room temperature.
Avoid exposure to direct sunlight and moisture to maintain sterility.
By following proper procedures and using flocked swabs, healthcare professionals can ensure accurate and reliable specimen collection, leading to better diagnostic outcomes and patient care.
The flocked swab tip is generally made of polyester (polyester), polyamide (nylon), and other chemical synthetic fibers from the flocking process.
View detailsThe vertical nylon fibers of the flocked nasopharyngeal swabs can improve sample collection rates and aid in the elution of the specimen into the t...
View detailsCommon Covid-19 test uses oropharyngeal sampling method, but in specific cases, the nasal sampling method is also used.
View detailsThe Mid-Turbinate Swab is an anatomically engineered collection device that specifically targets the mid-turbinate region of the nasal passageway, ...
View detailsWe value your privacy We use cookies to enhance your browsing experience, serve personalized ads or content, and analyze our traffic. By clicking "Accept All", you consent to our use of cookies.
Our Privacy Policy